Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are a subset of machine learning algorithms modeled after the human brain. These computational models consist of interconnecte...
Neural networks are computational models that mimic the human brain, crucial for AI and ML tasks such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and automation.
Neural networks simulate the human brain to analyze data, crucial for AI and ML. They consist of input, hidden, and output layers, using weights to learn patterns. Types include FNNs, CNNs, RNNs, and GANs, with applications in image and speech recognition.
A neural network, often referred to as an artificial neural network (ANN and discover their role in AI. Learn about types, training, and applications across various industries.")), is a computational model designed to simulate the way the human brain analyzes and processes information. It is a key component of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), particularly in deep learning, where it is used to recognize patterns, make decisions, and predict future outcomes based on data. Neural networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes, or artificial neurons, which process data through weighted connections, mimicking the synapses in a biological brain.
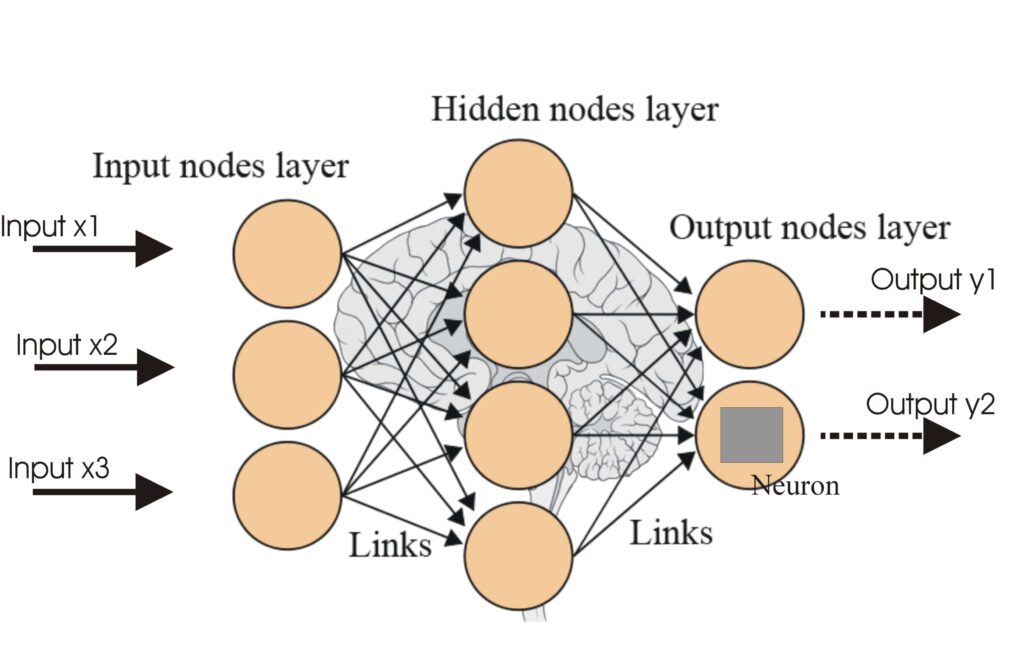
Neural networks are structured in layers, each serving a distinct role in processing information:
Each connection between nodes has an associated weight that signifies the strength of the relationship between nodes. During training, these weights are adjusted to minimize prediction error using algorithms like backpropagation.
Neural networks operate by passing data through their layers, each node applying a mathematical function to its inputs to produce an output. This process is typically feedforward, meaning data moves in one direction from input to output. However, some networks like recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have loops that allow data to be fed back into the network, enabling them to handle sequential data and temporal patterns.
Neural networks are used in a wide range of AI applications:
Training involves feeding the network vast amounts of data and adjusting the weights of the connections to minimize the difference between predicted and actual outcomes. This process is typically computationally intensive and requires powerful hardware, such as GPUs, to handle the large data sets involved.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
In the realm of AI automation and chatbots, neural networks enable systems to understand and generate human language, respond intelligently to user queries, and continuously improve their interactions through learning. They form the backbone of intelligent virtual assistants, enhancing their ability to provide accurate, context-aware responses that mimic human-like conversation. As AI technology advances, neural networks will continue to play an integral role in automating and enhancing human-computer interactions across various industries.
Neural Networks are a cornerstone of modern machine learning, providing frameworks for various applications ranging from image recognition to natural language processing bridges human-computer interaction. Discover its key aspects, workings, and applications today!"). Evelyn Herberg’s “Lecture Notes: Neural Network Architectures” offers a mathematical perspective on different Neural Network architectures, including Feedforward, Convolutional, ResNet, and Recurrent Neural Networks. These architectures are treated as optimization problems within the context of machine learning Read more. V. Schetinin’s work, “Self-Organizing Multilayered Neural Networks of Optimal Complexity,” explores the self-organization of neural networks to achieve optimal complexity, particularly under unrepresentative learning sets, with applications in medical diagnostics Read more. Firat Tuna introduces the concept of “Neural Network Processing Neural Networks” (NNPNNs) in his work, highlighting a new class of neural networks capable of processing other networks and numerical values, thus expanding their ability to interpret complex structures Read more. These studies underscore the dynamic nature of Neural Networks and their evolving complexity in addressing higher-order functions and problems.
A neural network is a computational model designed to simulate how the human brain processes information. It consists of interconnected layers of artificial neurons and is a foundational technology in artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Common types include Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), each suited for specific tasks like image recognition, sequence processing, and data generation.
Neural networks learn by adjusting the weights of connections between neurons based on the difference between predicted and actual outcomes, typically using algorithms like backpropagation and optimization techniques such as gradient descent.
They are widely used in applications such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, recommendation systems, autonomous systems, and chatbots.
Smart Chatbots and AI tools under one roof. Connect intuitive blocks to turn your ideas into automated Flows.
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are a subset of machine learning algorithms modeled after the human brain. These computational models consist of interconnecte...
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning in artificial intelligence (AI) that mimics the workings of the human brain in processing data and creating patter...
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a sophisticated class of artificial neural networks designed to process sequential data by utilizing memory of previous inp...