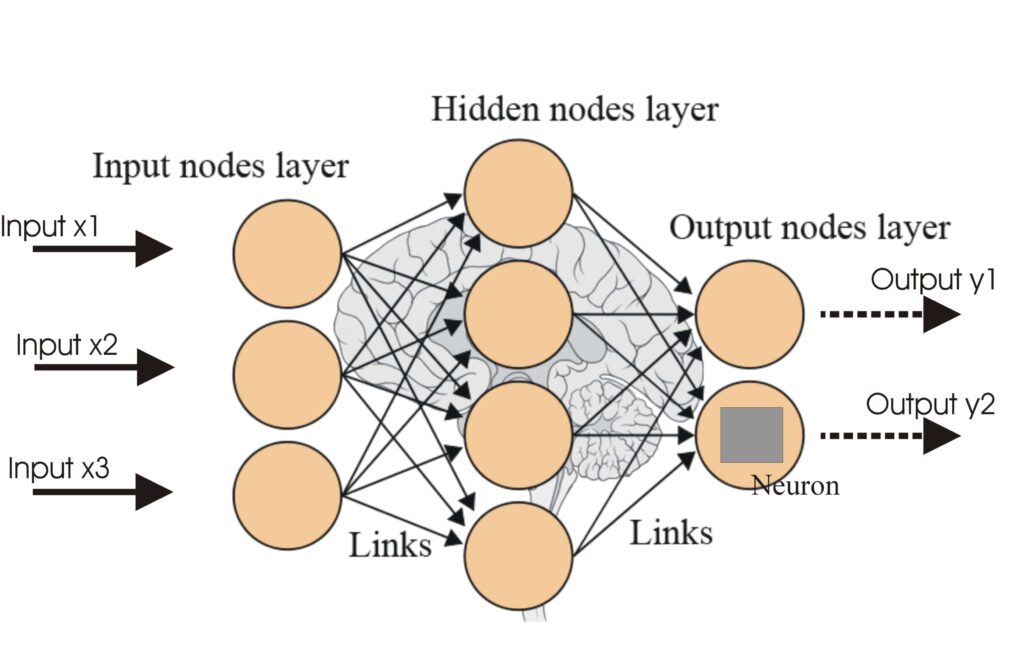
Neural Networks
A neural network, or artificial neural network (ANN), is a computational model inspired by the human brain, essential in AI and machine learning for tasks like ...
Neuromorphic computing mimics the structure and function of the human brain to create highly efficient, adaptive computer systems, revolutionizing AI and semiconductor technology.
Neuromorphic computing is a cutting-edge approach to computer engineering that models both hardware and software elements after the human brain and nervous system. This interdisciplinary field, also known as neuromorphic engineering, draws from computer science, biology, mathematics, electronic engineering, and physics to create bio-inspired computer systems and hardware.
Neuromorphic architectures are primarily modeled after neurons and synapses, which are considered the fundamental units of the brain. Neurons transmit information via chemical and electrical impulses, while synapses connect these neurons, facilitating the transfer of information. These biological structures are far more versatile, adaptable, and energy-efficient compared to traditional computer systems.
Neuromorphic computing leverages hardware that mimics the structures, processes, and functionalities of neurons and synapses in biological brains. The most common form of neuromorphic hardware is the spiking neural network (SNN). In these networks, artificial neurons process and hold data similarly to biological neurons, and synaptic devices use analog circuitry to transfer electrical signals that mimic brain signals.
Unlike standard computers that use binary systems to encode data, spiking neurons measure and encode discrete analog signal changes. This high-performance computing architecture is fundamentally different from the von Neumann architecture used in most modern computers.
Neuromorphic technology is expected to revolutionize various fields, including:
Neuromorphic processors have the potential to bypass the limitations of Moore’s Law, which predicts the exponential growth of transistors on a chip. As traditional semiconductor technology reaches its physical limits, neuromorphic computing offers a promising alternative.
The quest for AGI, an AI system that understands and learns like a human, is a significant driving force behind neuromorphic research. By replicating the human brain and nervous system, neuromorphic computing could pave the way for creating an artificial brain with the same cognitive abilities as a biological one, offering profound insights into cognition and consciousness.
Neuromorphic computing is an approach to computer engineering that designs hardware and software to mimic the structure and function of the human brain's neurons and synapses, creating highly energy-efficient and adaptive systems.
Unlike traditional computers that use binary-based architectures, neuromorphic systems use spiking neural networks and analog signals to process information in ways similar to biological brains, resulting in greater efficiency and adaptability.
Neuromorphic computing is used in advanced AI, deep learning, energy-efficient semiconductors, autonomous systems like robotics and self-driving cars, and is a potential path toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Yes, neuromorphic processors offer a promising alternative as traditional semiconductor technology approaches its physical limits, potentially enabling continued performance improvements beyond Moore’s Law.
Start building your own AI solutions using cutting-edge technologies like neuromorphic computing. Discover how FlowHunt can accelerate your projects.
A neural network, or artificial neural network (ANN), is a computational model inspired by the human brain, essential in AI and machine learning for tasks like ...
Cognitive computing represents a transformative technology model that simulates human thought processes in complex scenarios. It integrates AI and signal proces...
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are a subset of machine learning algorithms modeled after the human brain. These computational models consist of interconnecte...
